Intergate Vue in Django What Project Will We Build We want to build a vue project with multiple pages. The Django view render these pages as templates.
Why We Build Such A Project If we seperate frond-end and back-end and all routers are handled by the front-end project. The attackers can fake the reponse of authentication and jump to the target pages. If the attackers get the front-end code all in one package without authentication, they can parse out API easily.
So we consider to use front-end service to control the router and use back-end for access control.
Initial Repository 1 2 mkdir vid && cd vid git init
Create Virtual Environment Specify Python Version 1 pipenv --python ~/.pyenv/versions/3.7.1/bin/python3.7
Change Mirror (Optional) 1 2 3 4 [[source]] name = "pypi" url = "https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/" verify_ssl = true
Install Dependencies 1 pipenv install django==2.2.1
Start Django Project 1 2 3 pipenv run django-admin startproject vid mv vid vid-dir && mv ./vid-dir/* . && rmdir vid-dir # move project to current path pipenv run python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8000 # check django project works
Create Authorization API in Django You should always create a custom user model in Django. Here is why.
Remember not migrating until the custom user model is registered correctly.
Create Custom User Model First, let us create an app.
1 pipenv run python manage.py startapp account
We must install it in INSTALLED_APPS in settings.
1 2 3 4 5 6 INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'account' , ]
Then we need to create a custom user model.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from django.db import modelsfrom django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUserclass User (AbstractUser ): pass
And replace the default one by registering it.
1 2 3 AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'account.User'
After all, migrating the user model.
1 2 pipenv run python manage.py makemigrations pipenv run python manage.py migrate
Create Logining and Checking Views Let’s create class-based views with json responses.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import jsonfrom django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login, logoutfrom django.http import HttpRequest, HttpResponse, JsonResponsefrom django.views import Viewclass LoginView (View ): def post (self, request: HttpRequest ) -> JsonResponse: body = json.loads(request.body) user = authenticate(**body) if user is None : return JsonResponse(dict (status='error' , message='wrong password' )) login(request, user) return JsonResponse(dict (status='success' )) class GetUserInfoView (View ): def get (self, request: HttpRequest ) -> JsonResponse: user = request.user if not user.is_authenticated: return JsonResponse(dict (status='error' , message='not login' )) return JsonResponse(dict (status='success' ,data=dict (username=user.username))) class LogoutView (View ): def get (self, request: HttpRequest ) -> JsonResponse: user = request.user if not user.is_authenticated: return JsonResponse(dict (status='error' , message='not login' )) logout(request) return JsonResponse(dict (status='success' ))
Then, make router for it.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from django.urls import include, pathfrom .apis import LoginView, LogoutView, GetUserInfoViewurlpatterns = [ path('login/' , LoginView.as_view(), name='login' ), path('logout/' , LogoutView.as_view(), name='logout' ), path('get_user_info/' , GetUserInfoView.as_view(), name='get_user_info' ), ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from django.urls import include, pathurlpatterns = [ path('api/account/' , include('account.urls' )), ]
Creating Vue Project with Multiple Pages Initializing a Vue Project Frist of all, let us initialize a vue project.
1 2 3 vue create frontend cd frontend yarn install
Then we run the vue development service.
Open the URL show in terminal specified by our vue service. Make sure the vue project work well on it (usually localhost:8080).
Satisfication for Multiple Pages Move the entry into appropriate path.
1 2 3 4 # in the frontend directorymkdir -p src/pages/login mv main.js src/pages/login/app.js mv App.vue src/pages/login/app.vue
Change relative path in app.vue.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <!-- src/pages/login/app.vue --> <template> <div id="app"> <img alt="Vue logo" src="../../assets/logo.png"> <HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/> </div> </template> <script> import HelloWorld from '../../components/HelloWorld.vue' export default { // remove the 'name' field components: { HelloWorld } } </script> <!-- snipped -->
Copy a new page named “user”.
1 cp -r src/pages/login src/pages/user
Edit parameter msg in src/pages/user to make difference between pages.
1 2 3 4 <!-- snipped --> <HelloWorld msg="This Is The User Page"/> <!-- snipped -->
Create vue.config.js for build multiple pages.
1 2 # in the frontend directorytouch vue.config.js
Parsing and registering all pages in config file.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 'use strict' const titles = require ('./src/titles.js' )const glob = require ('glob' )const pages = {}glob.sync ('./src/pages/**/app.js' ).forEach (path => const chunk = path.split ('./src/pages/' )[1 ].split ('/app.js' )[0 ] pages[chunk] = { entry : path, template : 'public/index.html' , title : titles[chunk], chunks : ['chunk-vendors' , 'chunk-common' , chunk] } }) module .exports = { pages, chainWebpack : config =>plugins .delete ('named-chunks' ), }
Run the service again.
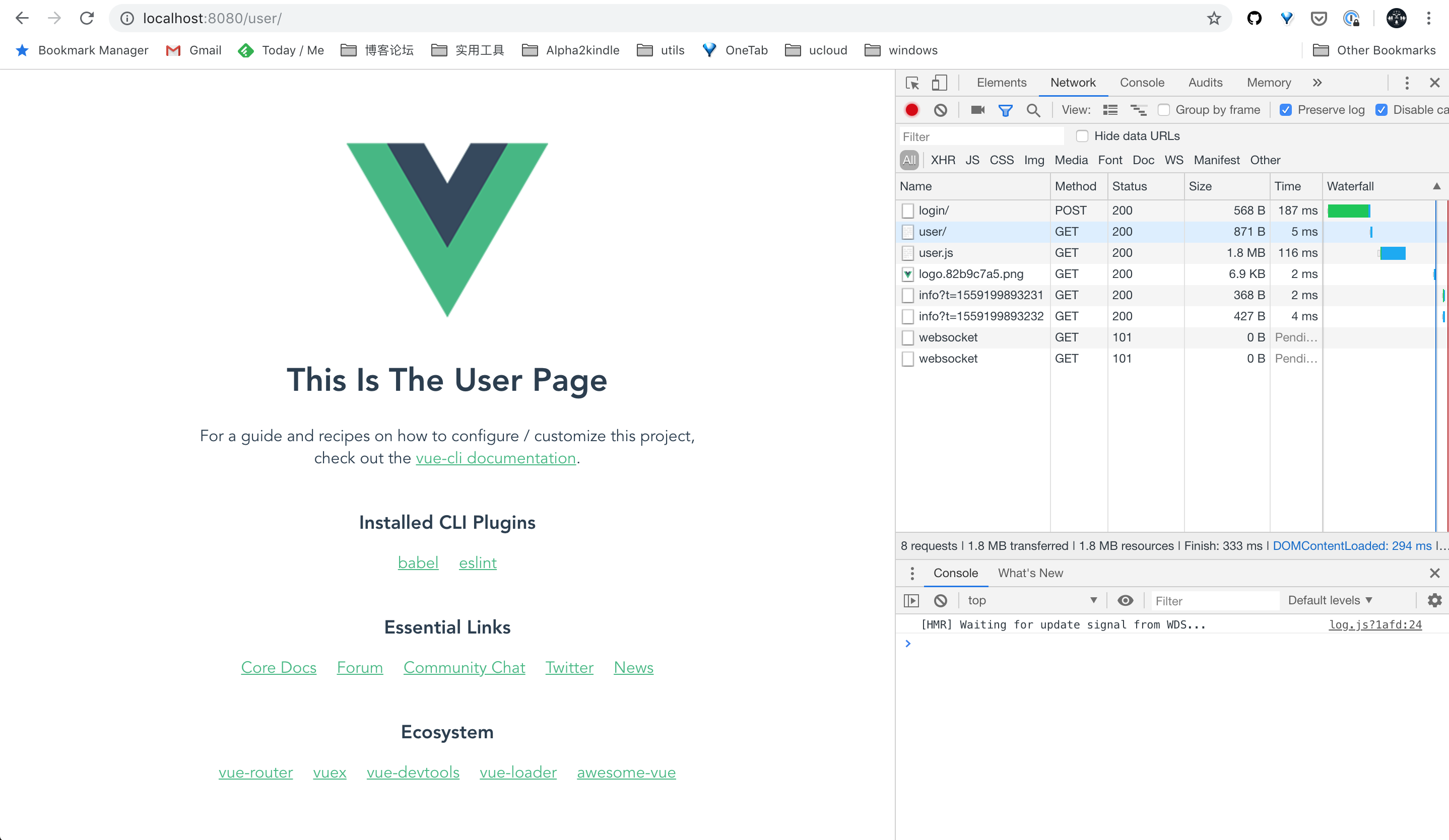
Now you can view the login and user pages corresponding url, such as localhost:8080/login/ and localhost:8080/user/.
Login page:
User page:
Inject Vue Page Into Django Template Build Vue Dist Build the vue project first.
And now, you get login.html and user.html in the path frontend/dist.
Show Login Page in Django View Let us show login page by TemplateView in Django.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from django.views.generic import TemplateViewurlpatterns = [ path('login/' , TemplateView.as_view(template_name='login.html' )), ]
Change template directory in settings.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TEMPLATES = [ { 'DIRS' : [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'frontend' , 'dist' )], }, ]
After Changing template path, the login view works well. But we find the static files is not found.
We setting assetsDir as 'static' in vue.config.js will ask vue-cli to build all assets in the same directory frontend/dist/static.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 module .exports = { assetsDir : 'static' , }
And then, registering the path in the Django settings.
1 2 3 4 5 STATICFILES_DIRS = [ os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'frontend/dist/static' ), ]
Now, we can rebuild the vue project and refresh the page.
After that, all files can be load correctly.
Render User Page Now, we already have the HTML file frontend/dist/user.html . Let us render it in a Django view.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 from django.http import HttpRequest, HttpResponse, HttpResponseRedirectfrom django.shortcuts import renderfrom django.urls import reversefrom django.views import Viewclass UserPageView (View ): def get (self, request: HttpRequest ) -> HttpResponse: if not request.user.is_authenticated: return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('login_page' )) return render(request, template_name='user.html' )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 urlpatterns = [ path('user/' , UserPageView.as_view(), name='user_page' ), ]
Let us try browsing the URL of user page (usually localhost:8000/user). Focus on the network tracks. We can see the request is redirected to the login page because we did not log in.
Create a Login Form in User Page First, let us install the ant design vue package. Here is the way to install and register ant design vue.
Import style in frontend/src/pages/login/app.js
1 import "ant-design-vue/dist/antd.css" ;
Create a new file in frontend/src/components, copy the login form from doc . Then:
import components from ant design vue
register components required
disable actions in mounted (optional)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 # frontend/src/components/LoginForm.vue <template> <a-form layout="inline" :form="form" @submit="handleSubmit" > <a-form-item :validate-status="userNameError() ? 'error' : ''" :help="userNameError() || ''" > <a-input v-decorator="[ 'userName', {rules: [{ required: true, message: 'Please input your username!' }]} ]" placeholder="Username" > <a-icon slot="prefix" type="user" style="color:rgba(0,0,0,.25)" /> </a-input> </a-form-item> <a-form-item :validate-status="passwordError() ? 'error' : ''" :help="passwordError() || ''" > <a-input v-decorator="[ 'password', {rules: [{ required: true, message: 'Please input your Password!' }]} ]" type="password" placeholder="Password" > <a-icon slot="prefix" type="lock" style="color:rgba(0,0,0,.25)" /> </a-input> </a-form-item> <a-form-item> <a-button type="primary" html-type="submit" :disabled="hasErrors(form.getFieldsError())" > Log in </a-button> </a-form-item> </a-form> </template> <script> import { Form, Button, Input, Icon } from 'ant-design-vue' import ant from 'ant-design-vue' console.log('ant', ant) // eslint-disable-line function hasErrors (fieldsError) { return Object.keys(fieldsError).some(field => fieldsError[field]) } export default { components: { 'a-button': Button, 'a-form': Form, 'a-form-item': Form.Item, 'a-input': Input, 'a-icon': Icon, }, data () { return { hasErrors, form: this.$form.createForm(this), } }, mounted () { this.$nextTick(() => { // To disabled submit button at the beginning. // this.form.validateFields() }) }, methods: { // Only show error after a field is touched. userNameError () { const { getFieldError, isFieldTouched } = this.form return isFieldTouched('userName') && getFieldError('userName') }, // Only show error after a field is touched. passwordError () { const { getFieldError, isFieldTouched } = this.form return isFieldTouched('password') && getFieldError('password') }, handleSubmit (e) { e.preventDefault() this.form.validateFields((err, values) => { if (!err) { console.log('Received values of form: ', values) } }) }, }, } </script>
Now we have a login form.
Using Axios to Send Login Request First let add proxy in vue project.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 module .exports = { # ----- snipped ----- devServer : { proxy : { '/api' : { target : 'http://127.0.0.1:8000' , changeOrigin : true , } } } }
Install Axios.
Have a try to request by Axios.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 // frontend/src/components/LoginForm.vue <script> import axios from 'axios' import { Form, Button, Input, Icon, message } from 'ant-design-vue' // ----- snipped ----- export default { methods: { handleSubmit (e) { e.preventDefault() this.form.validateFields((err, values) => { if (!err) { console.log('Received values of form: ', values) // eslint-disable-line this.login(values.userName, values.password) } }) }, async login (username, password) { let { data: { status, message: msg } } = await axios.post('/api/account/login/', {username, password}) if (status !== 'success') { message.error(msg) } else { window.location = '/user/' } } } </script>
You will find CSRF token error.
I do not find a better way to resolve it. Let disable CSRF token middleware until we find a solution.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # vid/settings.py MIDDLEWARE = [ # ----- snipped ----- # 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware' , # ----- snipped ----- ]
Create User and Test Redirection Let us create a user in django shell.
1 pipenv run python manage.py shell
1 2 3 In [1 ]: from account.models import User In [2 ]: User.objects.create_user(username='john' , email='john@vid.com' , password='weakpwd' ) Out[2 ]: <User: john>
And now we can use the account on vue service (usually localhost:8080/login/) go to the user page (usually localhost:8080/user/).
Rebuild Frontend and Have A Try in Django Service Now let’s rebuild the frontend.
1 2 # in frontend directoryyarn run build
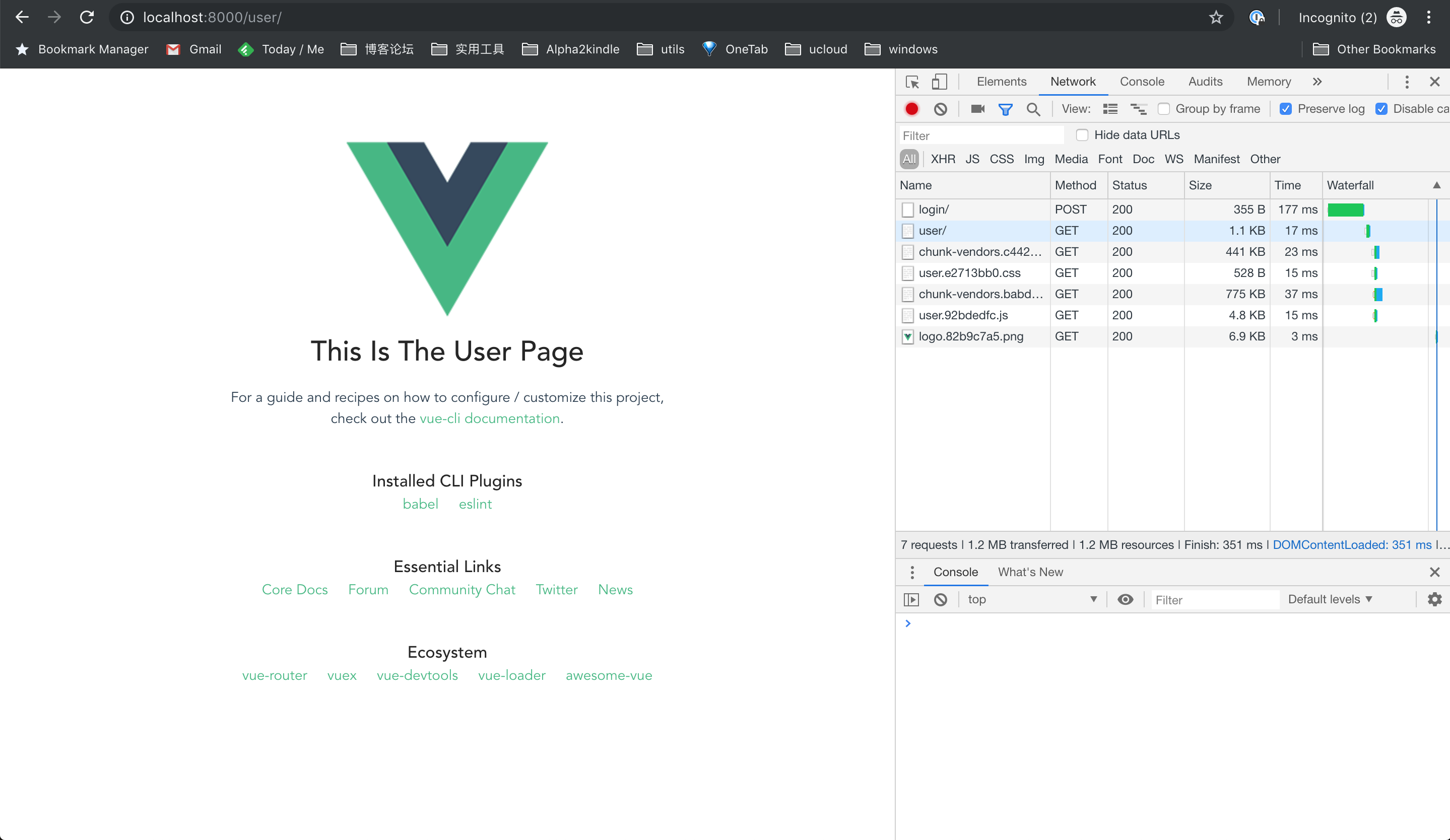
Now we can login and see the user page (localhost:8000/user/).
Reference: